About 70% of consumers say they've abandoned shopping carts due to a bad user experience (UX). Another 88% won't return to a website after a bad experience. Meanwhile, improving the UX on your site could boost conversions by up to 400%.
It can help improve your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts and organic rankings, too. To improve your rankings, you'll need to appeal to Google's Core Web Vitals.
Not sure how to improve your Core Web Vital metrics? Read on for the top tips you need to improve your SEO for websites today!
Upgrade WordPress Hosting
If your site loads slowly, you might want to upgrade your web hosting. For example, you might want to switch to a dedicated server.
WordPress hosting can impact your site's performance, influencing everything from security to page speed.
2. Implement a Caching Solution
Caching your web content will reduce the load on your server.
Caching tools can store HTML versions of each page. Content won't need to load every time a new visitor accesses your website.
Check your web host to determine if you can leverage caching at a server level. Some WordPress plans include server-side caching. You can also use plugins as a WordPress user, such as W3 Total Cache.
Other plugins include WP-Optimize, LiteSpeed Cache, and WP Fastest Cache. Consider consulting your SEO marketing agency before adding new plugins to your site. Unnecessary plugins can do more harm than good.
Partnering with an experienced marketing agency can help you make informed decisions regarding your SEO strategy and website UX.
These plugins can help reduce page load times, which can improve the user's online experience. If it takes too long for content to load, the user might leave. Your bounce rate will increase, which can hurt your organic rankings.
Using these plugins can ensure you cache database objects, CSS, JavaScript, pages, posts, and more.
Caching solutions can improve your First Input Delay (FID) score. The FID score indicates how long a user's browser takes to process event handlers as the visitor interacts with your site. In other words, FID measures the responsiveness of web pages when visitors interact with a page for the first time.
3. Defer JavaScript Loading
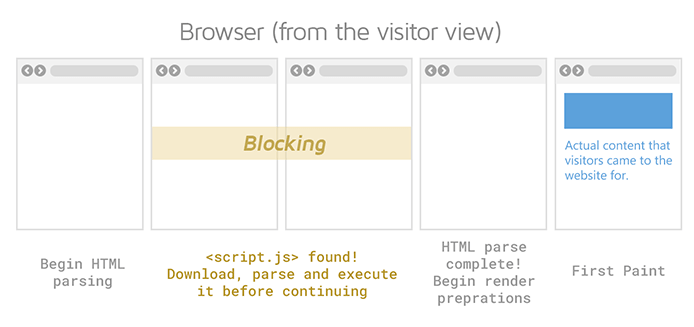
You can also improve your FID score by deferring the loading of JavaScript. This process is another method of eliminating render-blocking elements.
Deferring the loading of JavaScript can help web pages load faster. Once complete, other content on the page will load when visitors land on a page. They won't have to wait for all JavaScript files to load first.
You can also configure site settings to ensure critical CSS loads above the fold (all elements on the web page that appear first).
4. Use a Content Delivery Network
Consider using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to further improve your website UX. A CDN is a network of servers around the globe you can store content on. The CDN will serve site content from servers in the closest proximity to each individual visitor, increasing load times.
Using a CDN can improve your Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) times, minimizing the Time to First Byte (TTFB). LCP considers how long it takes for the main content to load when a visitor arrives. It considers how quickly the largest page element loads.
Over 50% of mobile site visitors will leave a page if it takes over three seconds to load. Improving load times can further improve the UX. Otherwise, visitors will leave, causing your bounce rate to increase.
5. Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources
Render-blocking elements include static HTML, JavaScript, and CSS files required to render a web page. Each file contains scripts that can prevent users from viewing content. Usually, they're created from tools like Google Analytics or third-party plugins.
Unfortunately, these scripts can hurt the user experience and your Core Web Vital metrics.
Try eliminating render-blocking resources. Minify and remove unused CSS or scripts as well.
For example, you can minify JavaScript and CSS by eliminating white space. Consider using tools like CSS Minifier to get started. You can input the CSS, click Minify, and replace the code.
You can also condense JavaScript and CSS by combining files.
6. Implement Lazy Loading
Lazy loading ensures images load exactly when the user gets to that section of the web page. Otherwise, everything will load at the same time as all other page elements, causing delays.
Choosing lazy loading can benefit your LCP score and loading speed.
Look for plugins like Smush that offer lazy loading features.
7. Size and Optimize Images
Optimize and compress images on your site to reduce their file sizes. You can use image compression tools like:
Imagify
Smush
EWWW Image Optimizer
ShortPixel
TinyPNG
These tools will reduce the file size without impacting image quality.
When you upload new images to your site, the Content Management System (CMS) will automatically assign image dimensions. Optimize your images by confirming they're the appropriate sizes and dimensions.
Define specific dimensions by adding the right attributes to help the browser allocate the appropriate amount of space for each page element.
8. Optimize Fonts
The fonts on your website can impact loading times, too. The browser will need to download and load the font family as the page loads. You can optimize web fonts to improve your website's performance and load times.
Try to remain selective about the fonts you use on your site. If you're using over two fonts, use global fonts to apply types and weights instead.
Rank Up: Appeal to Google's Core Web Vitals for SEO Success
Neglecting the user experience across your site can impact your SEO. Following Google's Core Web Vitals can improve the UX, and with it, your organic rankings. Higher organic rankings can help you reach new customers as they search for your offerings.
Improve your Core Web Vital metrics using these easy tips today.
Need more help? We're happy to lend a hand.
Contact our team today to learn more.